A Pinched Nerve in your Lower Back
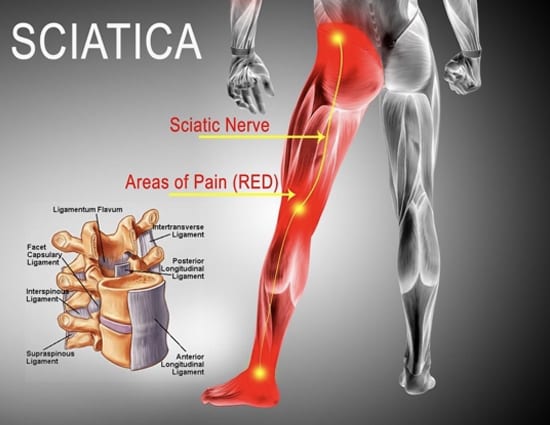
What is sciatica?
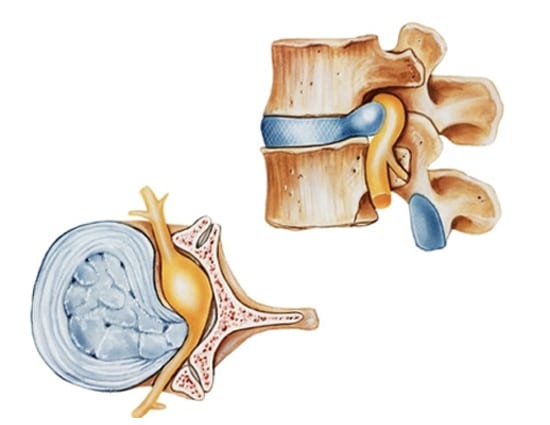
The lumbar spine includes 5 (L1-L5) vertebrae and associated intervertebral disks in the lower back. The vertebrae provide support and structure while the intervertebral disks act as shock absorbers between the vertebrae.
Nerve roots exit the spinal column at each level. Sciatica is inflammation of the sciatic nerve usually caused by pressure on the nerve root as it exits the spinal cord.
How does it occur?
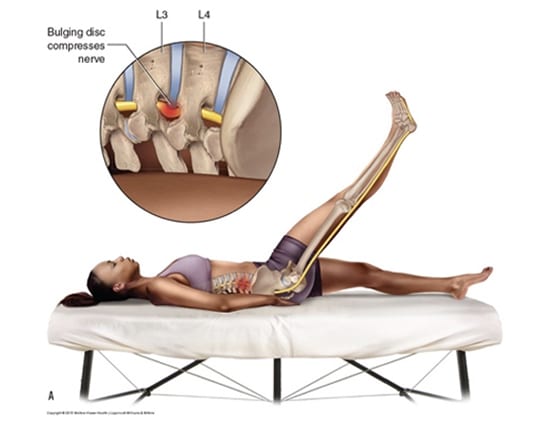
Sciatica generally occurs due to nerve root compression from an arthritic bone spur or more commonly from a herniated disk in the lower back.
Occurrences increase with age, obesity, twisting with heavy loads, diabetes, and prolonged sitting.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms are typically unilateral pain, weakness, tingling from the lower back radiating down the leg past the knee to the foot. This can be described as sharp, stinging, tingling, or burning pain.
How is it diagnosed?
Diagnosis can be done with a thorough patient history and physical exam. X-rays can show arthritic changes as well as disk space narrowing and alignment. CT/CT myelogram or MRI may be used to visualize soft tissues. An EMG or nerve conduction test can test the nerve function and confirm compression of the nerve root or spinal cord.
How is it treated?
Sciatica can be treated conservatively in many cases. Tylenol with an NSAID (Advil/ibuprofen, Aleve/naproxen, or a prescription arthritis medication are usually tried first to relieve pain and inflammation. Physical therapy may be beneficial. A stronger, short course of an oral steroid can be used to reduce inflammation in more severe cases. Muscle relaxers can be prescribed to relieve painful muscle spasms. Ice can be used for inflammation, and heat can be used for muscle spasms or soreness.
If these more conservative measures fail, the next step may be a steroid injection around the spine called an epidural block. These can be given in a series of up to 3 injection over the course of several weeks.
Rarely, in the most severe cases, or if symptoms do not get better in 4-6 weeks, surgery may be required. A laminectomy is a procedure where bone is removed to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. A foraminotomy is a procedure which removes bone around the nerve root, relieving pressure on that nerve root. A discectomy and fusion is a procedure where the herniated disk is removed and the vertebrae are fused together with hardware and bone graft.
What is the recovery time?
Conservative treatment of milder cases may take 6-8 weeks with medications and physical therapy.
Epidural blocks may be given in a series of up to 3 injections, spaced out a few weeks apart and can give weeks to months of relief.
Surgery may be done as a same day surgery or with a 1 night stay in the hospital, with lighter duty for 4-6 weeks, and a full recovery in 2-3 months. You may need to wear a neck brace during the recovery process.
We are here to help. If you believe you are suffering from one of these conditions, we would love to deliver a diagnosis, get you treated and get you moving again.


