Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great range of motion in your arm. Because so many different structures make up the shoulder, it is vulnerable to many different problems. The rotator cuff is a frequent source of pain in the shoulder.
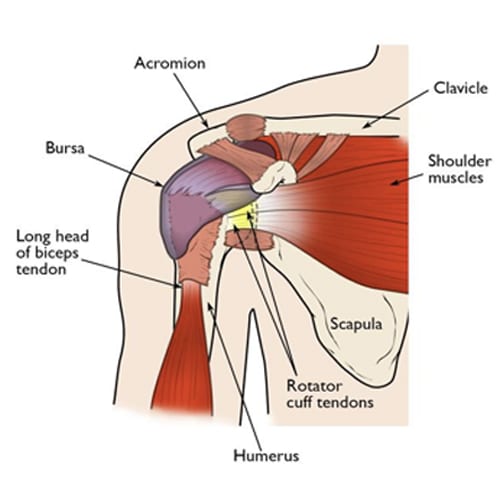
This illustration of the shoulder highlights the major components of the joint.
Anatomy
Your shoulder is made up of three bones:
- your upper arm bone (humerus),
- your shoulder blade (scapula), and
- your collarbone (clavicle).
Your arm is kept in your shoulder socket by your rotator cuff. These muscles and tendons form a covering around the head of your upper arm bone and attach it to your shoulder blade.
There is a lubricating sac called a bursa between the rotator cuff and the bone on top of your shoulder (acromion). The bursa allows the rotator cuff tendons to glide freely when you move your arm.
Description
The rotator cuff is a common source of pain in the shoulder. Pain can be the result of:
- Tendonitis. The rotator cuff tendons can be irritated or damaged.
- Bursitis. The bursa can become inflamed and swell with more fluid causing pain.
- Impingement. When you raise your arm to shoulder height, the space between the
acromion and rotator cuff narrows. The acromion can rub against
(or “impinge”on) the tendon and the bursa, causing irritation and pain.
Cause
Rotator cuff pain is common in both young athletes and middle-aged people. Young athletes who use their arms overhead for swimming, baseball, and tennis are particularly vulnerable. Those who do repetitive lifting or overhead activities using the arm, such as paper hanging, construction, or painting are also susceptible. Pain may also develop as the result of a minor injury. Sometimes, and sometimes occurs with no apparent cause.
Symptoms
Rotator cuff pain commonly causes local swelling and tenderness in the front of the shoulder. You may have pain and stiffness when you lift your arm. There may also be pain when the arm is lowered from an elevated position.
Beginning symptoms may be mild. Patients frequently do not seek treatment at an early stage. These symptoms may include:
- Minor pain that is present both with activity and at rest
- Pain radiating from the front of the shoulder to the side of the arm
- Sudden pain with lifting and reaching movements
- Athletes in overhead sports may have pain when throwing or serving a tennis ball
As the problem progresses, the symptoms increase:
- Pain at night
- Loss of strength and motion
- Difficulty doing activities that place the arm behind the back, such as buttoning or zippering
If the pain comes on suddenly, the shoulder may be severely tender. All movement may be limited and painful.
Doctor Examination
Medical History and Physical Examination
After discussing your symptoms and medical history, your doctor will examine your shoulder. He or she will check to see whether it is tender in any area or whether there is a deformity. To measure the range of motion of your shoulder, your doctor will have you move your arm in several different directions. He or she will also test your arm strength.
Your doctor will check for other problems with your shoulder joint. He or she may also examine your neck to make sure that the pain is not coming from a “pinched nerve,” and to rule out other conditions, such as arthritis.
Imaging Tests
Other tests which may help your doctor confirm your diagnosis include:
- X-rays. Because x-rays do not show the soft tissues of your shoulder like the rotator cuff, plain x-rays of a shoulder with rotator cuff pain are usually normal or may show a small bone spur. A special x-ray view, called an “outlet view,” sometimes will show a small bone spur on the front edge of the acromion.
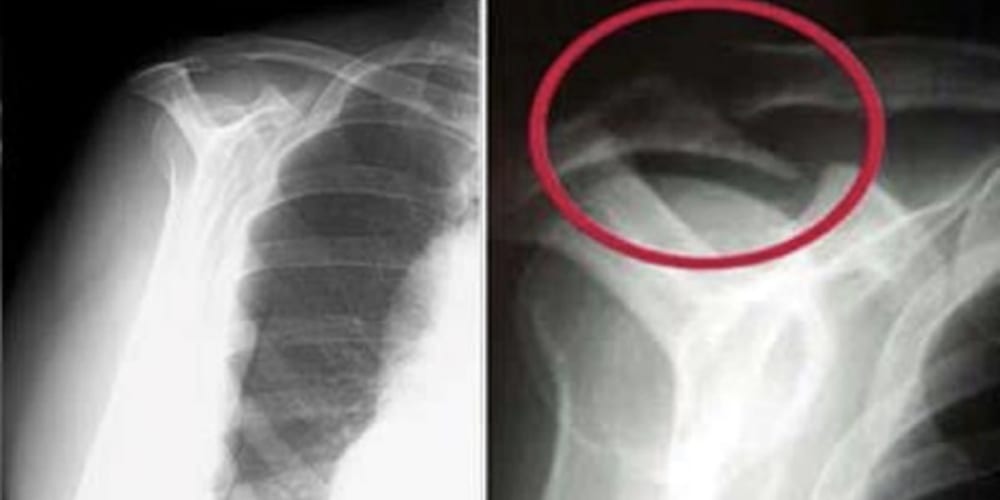
(Left) Normal outlet view x-ray. (Right) Abnormal outlet view showing a large bone spur causing impingement on the rotator cuff.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound. These studies can create better images of soft tissues like the rotator cuff tendons. They can show fluid or inflammation in the bursa and rotator cuff. In some cases, partial tearing of the rotator cuff will be seen.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce pain and restore function. In planning your treatment, your doctor will consider your age, activity level, and general health.
Nonsurgical Treatment
In most cases, initial treatment is nonsurgical. Although nonsurgical treatment may take several weeks to months, many patients experience a gradual improvement and return to function.
Rest. Your doctor may suggest rest and activity modification, such as avoiding overhead activities.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines. Drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen reduce pain and swelling.
Physical therapy. A physical therapist will initially focus on restoring normal motion to your shoulder. Stretching exercises to improve range of motion are very helpful. If you have difficulty reaching behind your back, you may have developed tightness of the posterior capsule of the shoulder (capsule refers to the inner lining of the shoulder and posterior refers to the back of the shoulder). Specific stretching of the posterior capsule can be very effective in relieving pain in the shoulder.
Once your pain is improving, your therapist can start you on a strengthening program for the rotator cuff muscles.
Steroid injection. If rest, medications, and physical therapy do not relieve your pain, an injection of a local anesthetic and a cortisone preparation may be helpful. Cortisone is a very effective anti-inflammatory medicine. Injecting it into the bursa beneath the acromion can relieve pain.
may relieve painful symptoms.
Surgical Treatment
When nonsurgical treatment does not relieve pain, your doctor may recommend surgery.
The goal of surgery is to create more space for the rotator cuff. To do this, your doctor will remove the inflamed portion of the bursa. He or she may also perform an anterior acromioplasty, in which part of the acromion is removed. This is also known as a subacromial decompression. These procedures can be performed using either an arthroscopic or open technique.
Arthroscopic technique. In arthroscopy, thin surgical instruments are inserted into two or three small puncture wounds around your shoulder. Your doctor examines your shoulder through a fiberoptic scope connected to a television camera. He or she guides the small instruments using a video monitor, and removes bone and soft tissue. In most cases, the front edge of the acromion is removed along with some of the bursal tissue.
Your surgeon may also treat other conditions present in the shoulder at the time of surgery. These can include arthritis between the clavicle (collarbone) and the acromion (acromioclavicular arthritis), inflammation of the biceps tendon (biceps tendonitis), or a partial rotator cuff tear.
Open surgical technique. In open surgery, your doctor will make a small incision in the front of your shoulder. This allows your doctor to see the acromion and rotator cuff directly.
Rehabilitation. After surgery, your arm may be placed in a sling for a short period of time. This allows for early healing. As soon as your comfort allows, your doctor will remove the sling to begin exercise and use of the arm.
Your doctor will provide a rehabilitation program based on your needs and the findings at surgery. This will include exercises to regain range of motion of the shoulder and strength of the arm. It typically takes 2 to 4 months to achieve complete relief of pain, but it may take up to a year.


